How to Learn Cybersecurity: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
In the current digital era, learn cybersecurity has undoubtedly become greater than before. Since there are cyber attacks every 39 seconds, it is important to know how to defend a system, a network, or any information from such dangers. This guide is designed to help you take the initial steps towards this noble purpose of defending our cyberspace, beginning from the basic fundamentals and advancing to the more sophisticated methods.
Key Skills Every Cybersecurity Professional Needs
Before getting into the details of learning cybersecurity, it would be wise to check out the basic skills that are needed in this domain. A good base will help both understand sophisticated ideas and become a most sought after professional.
-
Networking Knowledge:
It is very important to know different networking protocols and the way these networks transfer data. This knowledge will help enumerate the risks involved with different network architectures.
-
Programming and Scripting:
Knowledge of languages such as C, C++, and Python as well as scripting languages is quite important for writing targeted attacks and their supporting tools.
-
Cyber Security Basics:
Well, some understanding of the fundamentals of cybersecurity – for example, what a threat is, what a vulnerability is, what a risk is and what the security principles are – is self-evident.
-
Operating Systems:
All of that is helpful, as it helps one carry out the assessment of the system weaknesses as well as the system specific security configurations by utilizing knowledge of more than one operating systems such as Windows, Linux and Unix.
-
Web Application Security:
Understanding web technologies such as SQL injection and Cross site scripting and how they pose threats to web development protection is important.
-
Penetration Testing Tools:
It is important to have a high level of confidence of use of such tools, like Metasploit, Nmap and Burp Suite, when conducting vulnerability asses’s.
-
Cryptography:
Knowing how to encrypt and decrypt information and what cryptography entails is necessary since it involves data protection.
-
Wireless Security:
Knowledge of how to secure a wireless network or Wi-Fi related activities is paramount to safety of wireless communications.
-
Compliance and Standards:
Knowledge of information security standards and compliance and best practices like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and General Data Protection Regulation factors would be an advantage.
-
Incident Response:
Readiness to manage security incidents and breaches and possessing forensic and analytical skills is critical.
-
Social Engineering Awareness:
Knowing how attackers try to deceive people’s thinking in order to steal information is useful in avoiding data breaches.
-
Ethical Mindset:
It is compulsory for every cybersecurity expert to adhere to strict ethical principles and promote responsible disclosure policy.

Building Your Educational Foundation
To become a successful cybersecurity professional, a solid educational foundation is paramount. While formal education can provide essential knowledge, self-learning and practical experience are equally important.
Basic Education
Start by completing high school, focusing on subjects like mathematics, computer science, and information technology. These subjects are foundational as they teach you logical thinking and how computers work.
Higher Education
After high school, consider pursuing a degree in computer science, information technology, or cybersecurity. While a degree can help in gaining a solid foundation and is often preferred by employers, it is not the only path to becoming an ethical hacker. Many successful professionals have learned skills independently. Employers value problem-solving abilities and creativity over degrees.
Developing Essential Technical Skills
Once you have a solid educational background, the next step is to develop essential technical skills. This is where you will start building your hacker toolkit and preparing for hands-on learning experiences.
Programming
Programming is akin to learning a new language for communicating with computers. Start with Python due to its beginner-friendly nature, then progress to C and C++ for low-level operations, and JavaScript for web-based hacking. Practice by writing small scripts and automating tasks.
Networking
Understanding networking is crucial as it is where most hacking occurs. Learn about IP addresses, subnets, and protocols like TCP/IP. Set up your own network lab at home using virtual machines to experiment with different setups.
Operating Systems
Familiarize yourself with operating systems, particularly Linux, which is essential for many security tasks. Use distributions like Kali Linux and practice using Linux as your main OS.
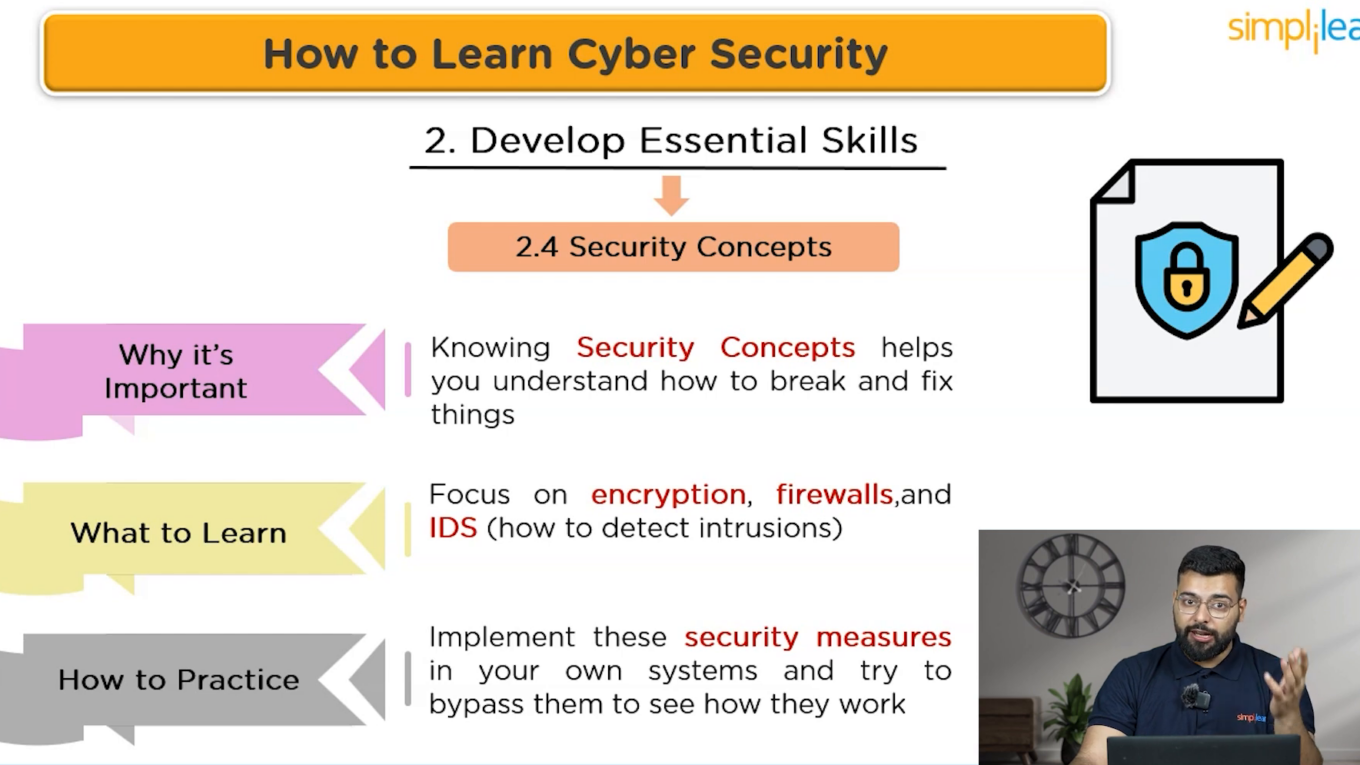
Security Concepts
Focus on core security concepts like encryption, firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems. Implement these measures in your own system and practice bypassing them to understand their functionality.
Certifications: Badges of Honor
Certifications are vital in the cybersecurity field, serving as proof of your knowledge and skills. They can open doors to job opportunities and validate your expertise.
- Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH): This certification covers the fundamentals of ethical hacking and teaches you the mindset and tools hackers use.
- CompTIA Security+: A great starting point for a career in cybersecurity, covering a wide range of security topics.
- Offensive Security Certified Professional (OSCP): Known for its hands-on practical approach, this certification requires you to perform hacking techniques in a controlled environment.
- Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): An advanced certification for those looking to move into higher-level security roles.

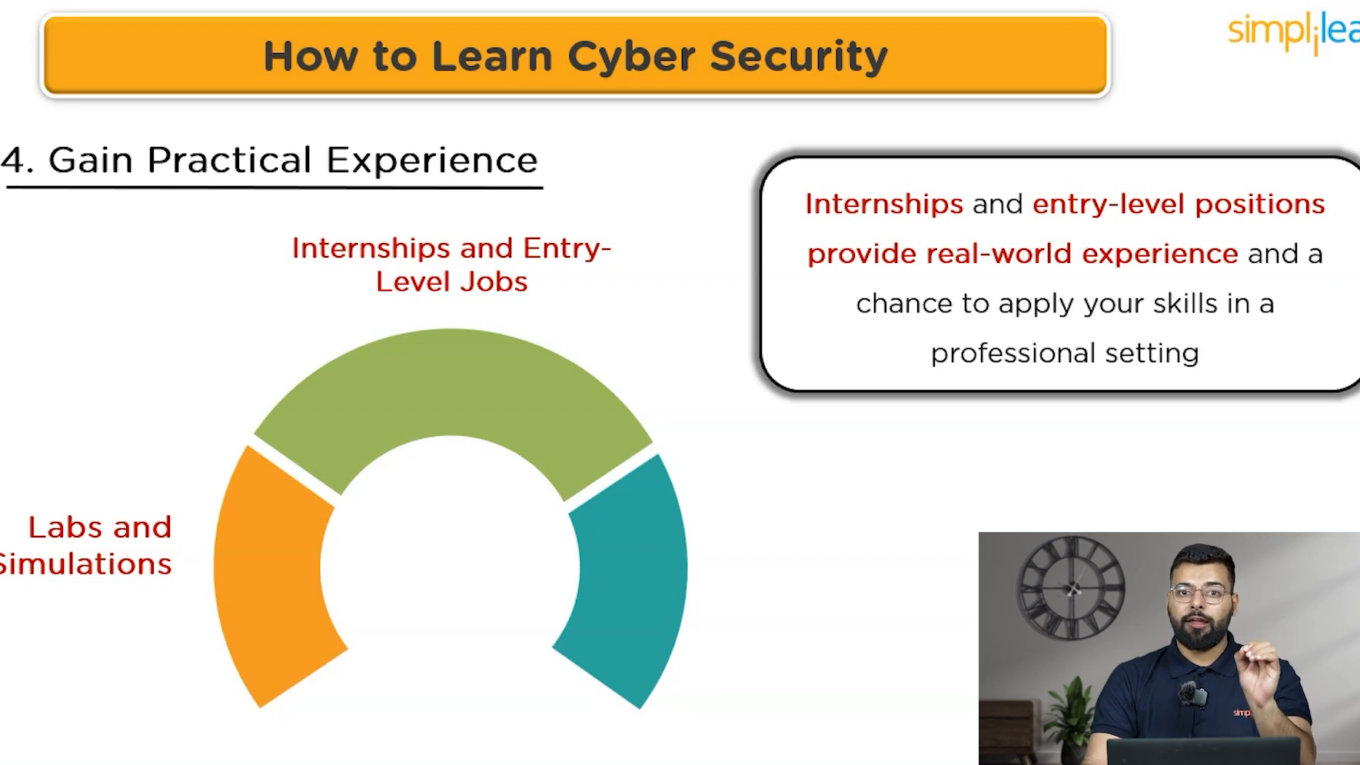
Gaining Practical Experience
Practical experience is where theory meets reality. It’s crucial to apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios to hone your skills effectively.
Labs and Simulations
Use platforms like Hack The Box, TryHackMe, and CyberSec Labs to practice hacking skills safely. These environments allow you to learn from your mistakes without legal repercussions.
Internships and Entry-Level Positions
Seek internships or entry-level jobs in IT network administration or cybersecurity. These roles will provide firsthand experience with the systems you will protect as an ethical hacker.
Bug Bounty Programs
Participate in bug bounty programs, where companies offer rewards for identifying security vulnerabilities in their systems. Platforms like HackerOne and Bugcrowd connect ethical hackers with companies offering these programs.
Staying Updated in Cybersecurity
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving. Staying informed about the latest trends, threats, and technologies is crucial for maintaining your edge.
Continuous Learning
Subscribe to cybersecurity news sites, blogs, and forums. Resources like Krebs on Security, Dark Reading, and the Reddit NetSec community are excellent for keeping up with developments.
Conferences and Workshops
Attend key conferences like DEF CON, Black Hat, and RSA Conference to learn about the latest trends and network with other professionals.
Online Courses
Consider enrolling in online courses from platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Cybrary to keep your skills sharp and up-to-date.
Joining the Cybersecurity Community
Being part of the cybersecurity community can greatly benefit your career. Networking with other professionals can provide valuable insights and job opportunities.
Networking
Engage with professional organizations like the Information Systems Security Association (ISSA) and the EC-Council. Attend meetings and participate in events to build your network.
Finding a Mentor
A mentor can provide guidance and share resources to help you navigate your career path. Look for experienced ethical hackers willing to share their knowledge.

Companies Hiring Ethical Hackers
Multiple sectors are always in need of proficient and ethical hackers. Some of the common employers include IT organizations, Information security companies, consultancies and banks.
- IT Companies: Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Facebook.
- IT Security Regional Offices: Palo Alto Networks, CrowdStrike.
- Management Consulting: Deloitte, PwC, KPMG.
- Financial Organizations: JPMorgan Chase and Bank of America.
State Institutions: NSA, FBI.
Job Roles and Salaries
Ethical hackers work as penetration testers, cybersecurity analysis, security consultants, security engineering or incident responders. The job descriptions suggest numerous salary packages based on location and the level of experience, however, beginning professionals in India usually make 4 to 6 lakhs per year and in the USA it is from 70000 to 90,000 dollars.

Conclusion
A career in cybersecurity is not for the faint-hearted; it demands hard work, learning and more practice. By understanding the fundamental requirements, acquiring the necessary competencies and undertaking relevant work experience, you will set yourself up for success in this vital career field. Having an attitude of never settling down or adopting complacency, being ready to learn and take risks seems exciting. This isn’t a space that has boundaries, as there are opportunities galore.
